Which of the Following Antibiotics Disrupts Cytoplasmic Membrane Function
FALSE Because all cells engage in protein synthesis there are few antimicrobial drugs that. Efflux pumps beta-lactamases and modification of porins all utilize membrane transport proteins.
The PBP interacts with β-lactam ring and are not available for the synthesis of new peptidoglycan.
. Which of the following is a primary advantage of semisynthetic drugs. Whilst it is well established that colistin disrupts the bacterial outer membrane OM by selectively targeting lipopolysaccharide LPS. Which antibiotics disrupt the cytoplasmic membrane function.
A Those that disrupt cell membrane function b Those that inhibit nucleic acid function c Those that affect the cell wall d Those that inhibit protein synthesis e Those that inhibit nucleic acid synthesis A new antibiotic binds to the sigma factor of gram negative bacteria thus interfering with. A large percentage of antibiotics and semisynthetic drugs are produced by members of the genus. This communication introduces a potent antibiotic that disrupts bacterial membranes.
Penicillin vancomycin1- Penicillin or other cell wall synthesis inhibitor is added to the growth medium with a dividing bacterium2- The cell begins to grow but is unable to synthesize new cell wall to accommodate the expanding cell3-. Beta-lactam drugs act by inhibiting formation of the cytoplasmic membrane. Causes mismatches between codons and anticodons leading to faulty proteins that insert into and disrupt cytoplasmic membrane.
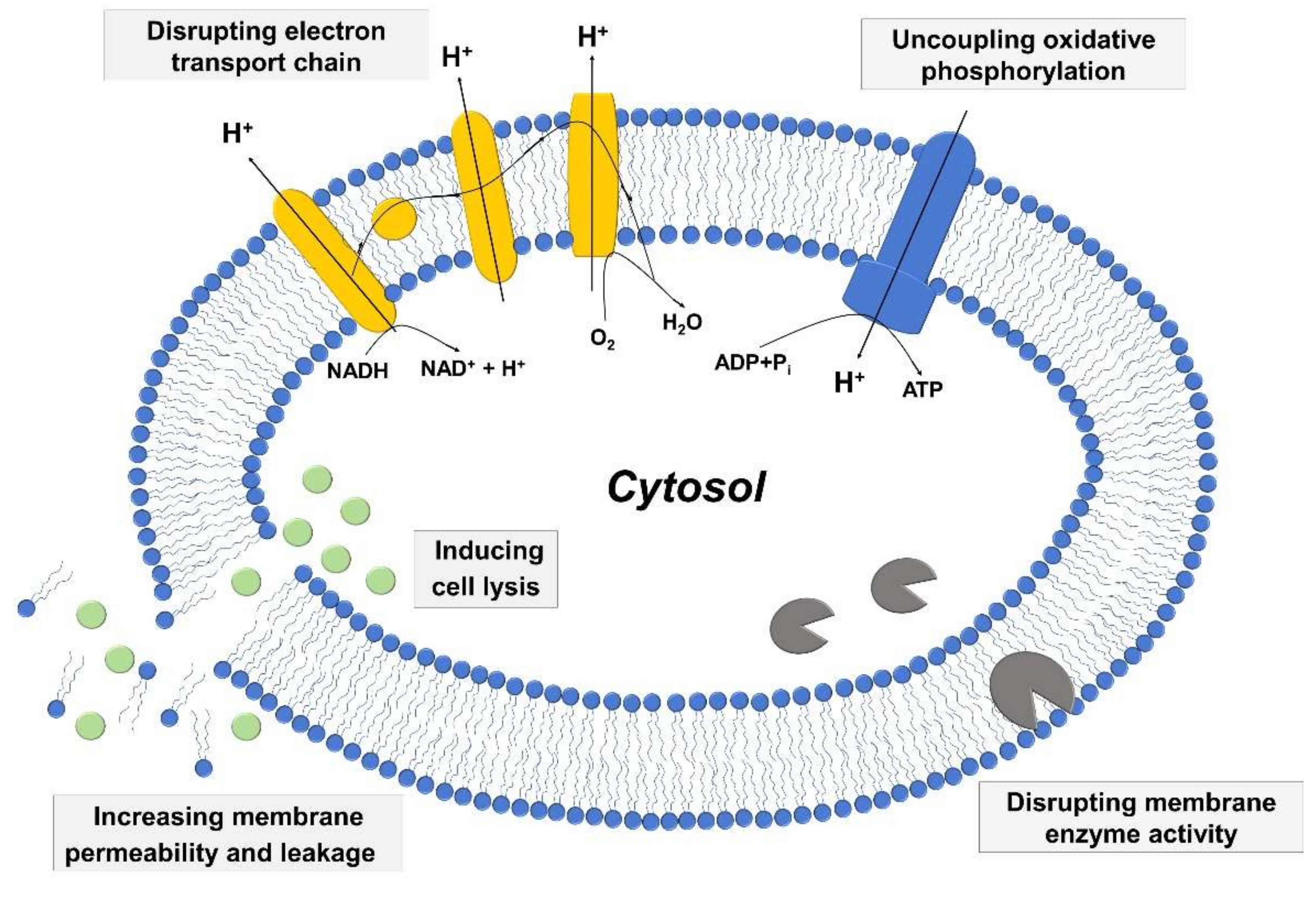
Most prominent was the induction of genes belonging to the general cell wall stress stimulon Table 1 a group of genes that are induced following treatment with cell wall active antibiotics such as vancomycin oxacillin d-cycloserine and Bacitracin 38 40 and with CM depolarizing agents such as daptomycin and cationic defense peptides. The primary targets of the β-lactam agents are the PBPs. Daptomycin which targets both membrane function and peptidoglycan synthesis is especially effective in treating staphylococcal infections.
To conduct the assay bacteria were grown overnight in LB and sub-cultured 1100 in LB supplemented 125 mM CaCl 2 05 mM MgCl 2 and 02 glucose. A Cellular respiration d Translation 2 b. Aureus ATCC 25923 as a model organism 282937.
2-3-36-dichloro-9H-carbazol-9-yl-2-hydroxypropylamino-2-hydroxymethylpropane-13-diol which we refer to as DCAP. E A amphotericin B. Which Antibiotics disrupts cell membrane in bacteria.
Which of the following antibiotics disrupts cytoplasmic membrane function. Blocks association of tRNAs with ribosome. Diagram depicting the failure of bacterial cell division in the presence of a cell wall synthesis inhibitor eg.
Recently fosfomycin has been used in the treatment of multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria. A streptomycin B erythromycin C tetracycline D penicillin E amphotericin B Answer. Streptomycin gentamicin neomycin kanamycin.
When antibiotic therapy disrupts the normal microbiota which 2 things can occur. Cytoplasmic Membrane Fluidity Assay. A penicillin B erythromycin C amphotericin B D tetracycline E streptomycin.
Amphotericin B is. Colistin is an antibiotic of last resort but has poor efficacy and resistance is a growing problem. Which of the following antibiotics disrupts cytoplasmic membrane function.
They have a broader spectrum of action. What is the mode of action of the Polyene family of antifungal antibiotics eg. Penicillin disrupts the cell wall which is located outside of the cell membrane.
In contrast to growth-based antimicrobial agents membrane-targeting drugs effectively kill slow-growing bacteria. Penicillin is an example. Membrane transport proteins are required for which modes of antibiotic resistance.
Which of the following antibiotics disrupts cytoplasmic membrane function. The bacteria were grown. It disrupts the pedtidoglycan of the cell membrane in Gram-positive bacteria.
It has been hypothesized that the β-lactam ring mimics the D-alanyl D-alanine portion of peptide chain that is normally bound by PBP. Which of the following antibiotics disrupts cytoplasmic membrane function. Laurdan dye was used to assess membrane fluidity as previously described using S.
6 Which of the following antibiotics disrupts cytoplasmic membrane function. Which of the following drugs specifically targets cell walls that contain arabinogalactan-mycolic acid.

Mechanisms Of Antibacterial Drugs Microbiology
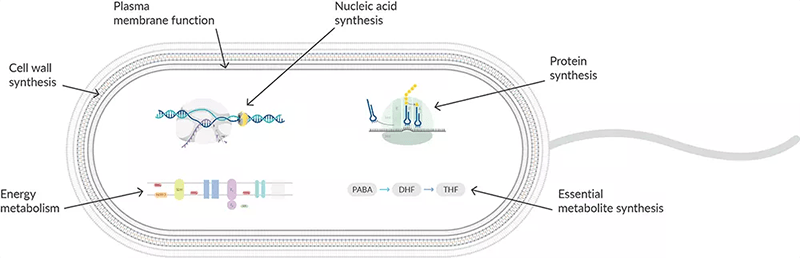
How Do Antibiotics Affect Plasma Membrane Function Biomol Blog Resources Biomol Gmbh Life Science Shop

Cellular Targets Of Antifungal Agents The Antifungal Agents Target Download Scientific Diagram

Various Liposomes Formulations And Their Effect As Antimicrobial Drug Download Table

Ijms Free Full Text Antibacterial Free Fatty Acids And Monoglycerides Biological Activities Experimental Testing And Therapeutic Applications Html
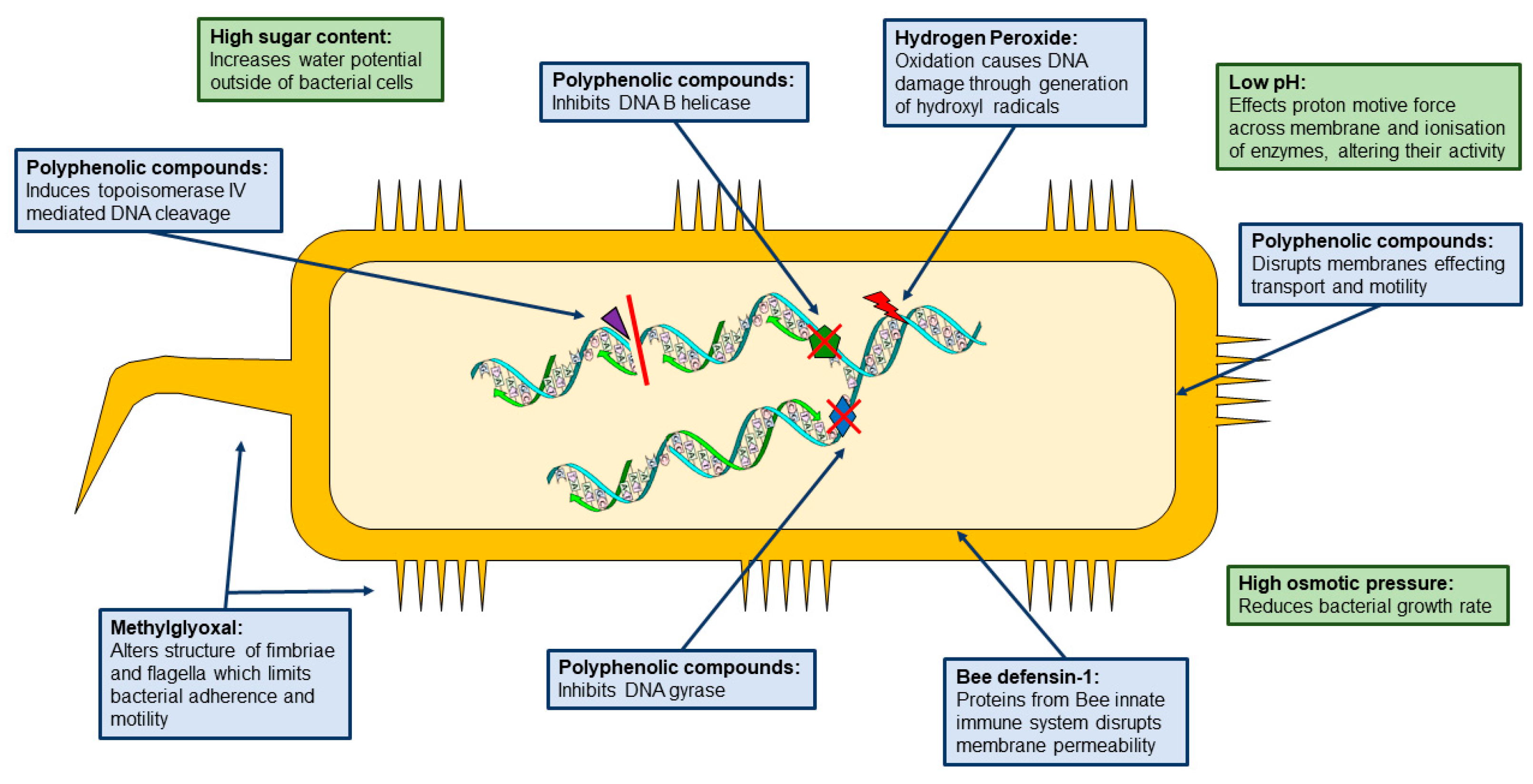
Antibiotics Free Full Text Dissecting The Antimicrobial Composition Of Honey Html

Antimicrobial Compounds Produced By Food Grade Bacteria Download Table

Antimicrobial Compounds Produced By Food Grade Bacteria Download Table
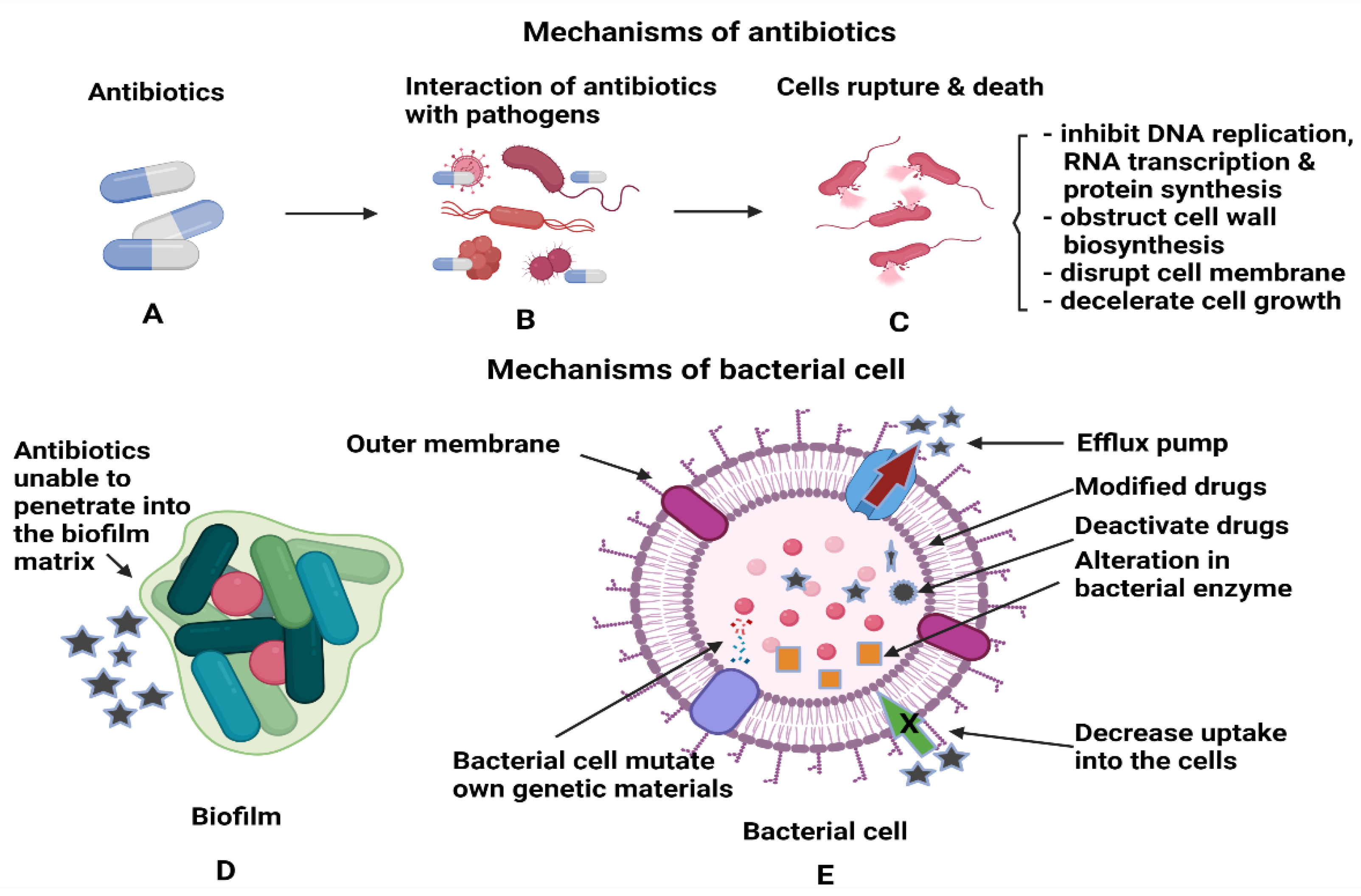
Antibiotics Free Full Text Potential Of Nanoparticles Integrated With Antibacterial Properties In Preventing Biofilm And Antibiotic Resistance Html

No comments for "Which of the Following Antibiotics Disrupts Cytoplasmic Membrane Function"
Post a Comment